To restore your sex life to its former glory and treat pelvic pain during sex effectively, you need to find and fix the root cause.
When women experience pain in the genital region before or after sex, we call it “Dyspareunia.”
This type of pain can be in the vagina, the vulva, the pelvis, or the uterus.
There are some medical reasons why sex could be painful for you, including infection or another medication condition.
However, pelvic pain during sex is most likely an issue with your pelvic floor muscles or the surrounding structures, which we can resolve with physical therapy.
More Blogs From Universus:
How Can I Get Effective Pain Relief For My Arthritis?
What Are The Warning Signs Your Partner Has Pelvic Problems?
Maintaining Strength As You Get Older
What Is Dyspareunia?

Although pain is usually limited to the genital region, many women feel pain during and after sexual intercourse in the vulvar and the vaginal opening or internally in the lower abdomen, uterus, and cervix.
Unfortunately, this type of pain doesn’t just affect you physically.
It can also affect women psychologically and emotionally by sabotaging their self-confidence, reducing sexual intimacy (or stopping it altogether), and damaging their relationships (sometimes irrevocably).
Who is more likely to experience Dyspareunia?
Pain during sexual intercourse is common in women.
However, “dyspareunia” can affect both genders and all age groups.
Painful sex is one of the most common gynecological issues treated by healthcare providers, with around 10-20% of the US population experiencing it at some stage of their life.
Where Does It Hurt?

Although pain is usually limited to the genital region, many women feel pain during and after sexual intercourse in the vulvar and the vaginal opening or internally in the lower abdomen, uterus, and cervix.
Unfortunately, this type of pain doesn’t just affect you physically.
It can also affect women psychologically and emotionally by sabotaging their self-confidence, reducing sexual intimacy (or stopping it altogether), and damaging their relationships (sometimes irrevocably).
Who is more likely to experience Dyspareunia?
Pain during sexual intercourse is common in women.
However, “dyspareunia” can affect both genders and all age groups.
Painful sex is one of the most common gynecological issues treated by healthcare providers, with around 10-20% of the US population experiencing it at some stage of their life.
Where Does It Hurt?

We classify painful intercourse into four different types of pain:
Primary: Those that are new to sex and experiencing pain
Secondary: Pain that occurs after sex
Complete: pain that occurs every time you have sex
Situational: Pain that only happens at certain times or certain situations
In addition, the location where you feel the pain before or after sex gives us a clue as to why you might be experiencing the pain. For instance:
Entry pain: Also referred to as superficial Dyspareunia or intraorbital pain, entry pain occurs at the entrance to the vagina in the early stages of penetration.
Some reasons for this type of pain may be infection, injury, tight pelvic floor muscles, or insufficient lubrication.
Deep pain: Also known as “collision dyspareunia,” this pain occurs with deep vaginal penetration and may be worse in certain sexual positions.
The pain is usually in the lower abdomen or the cervix region.
The cause of deep pain may be tight pelvic floor muscles, pelvic organ prolapse, or previous surgery or medical issue.
What Causes Pelvic Pain During Sex?
Many women feel pain during sex due to a lack of sufficient lubrication. One way to solve this issue is to use a lubricant.
But even more often than a lack of lubrication, tight pelvic floor muscles cause pain during sex.
To resolve this issue, you can learn to relax your pelvic floor (with the help of a physical therapist) and increase the time you dedicate to foreplay.
Other less common causes for painful intercourse could be any one of the following:
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): When the tissues inside your pelvic region are inflamed (as is the case with pelvic inflammatory disease). It can cause pain during and after sexual intercourse. If PID is the cause, you will feel pain deep inside the pelvis.
Infections: A yeast infection is one of the most common causes of pelvic pain during sex, especially among women. But a yeast infection is likely to have other symptoms, not just painful sex, such as redness, itchiness, and inflammation along with the tell-tale thick white discharge.
Vaginal atrophy: When the lining of the vagina is thin, dry, and inflamed, we call it “vaginal atrophy.” Vaginal atrophy is usually the result of the hormonal changes accompanying perimenopause and menopause. But it can also be caused by some medications or occur naturally.
Issues with the cervix: The penis can sometimes touch the cervix during deep penetration. If you have an infection or other gynecological problem in this area, sex can cause pain.
Prolapse: A pelvic organ prolapse is when one or more of your pelvic organs, such as the bowel, bladder, or uterus, drop down (or bulge) into or out of the vagina. Weak pelvic floor muscles and pelvic organ prolapse are significant causes of painful sex. If you feel something bulging into or out of your vagina, you should consult a physical therapist for help.
Vaginismus: For women who have endured sexual trauma or have any other type of fear associated with sex, sex can be painful. This pain is most often due to muscle spasms in the vagina. The treatment for vaginismus is individual, but a combination of talking therapy and pelvic floor physical therapy can be effective.
Endometriosis: This painful medical condition causes the tissue lining of the uterus (endometrium) to develop outside the uterus. It can also cause additional pain during and after sexual intercourse and throughout the menstrual cycle. Physical therapy can help reduce the frequency and intensity of endometriosis-related pain.
Fibroids: These benign growths occur in and around the uterus – and can grow to the size of a grapefruit. They can also cause pain during sexual intercourse.
Cysts in the ovaries: When ovarian cysts develop with or without Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), they can lead to discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse.
STIs (sexually transmitted infections): Any sexually transmitted disease, like herpes, genital warts, etc., can make intercourse painful.
Injury to the vagina or vulva: Any damage to the vagina or vulva, like an incision to the perineum during labor or a tear (episiotomy) from childbirth, can make having intercourse painful. If your issues started after delivery, we recommend that you consult a physical therapist and pelvic floor specialist to determine what’s going on and to help you fix the problem.
Psychological: Victims of sexual abuse sometimes find it painful to have sex. Depression and anxiety, and some forms of medication, can also prevent sexual arousal and result in a lack of lubrication and pain during sex. The psychological effects of traumatic childbirth can also cause sex to be difficult and painful. Talking therapy in combination with physical therapy can be helpful.
Premature intercourse: Starting intercourse immediately after childbirth or surgery can cause pain. Doctors advise that you wait a minimum of 6-8 weeks before starting to have intercourse. Even after that, it should be gentle with adequate foreplay and lubrication. If you are breastfeeding, you can sometimes have lower estrogen levels, which can cause vaginal dryness. If there is dryness, choose a water-based lubricant, as they are safer.
Vulvodynia: is a chronic pain condition that develops in the vulva region. Physical therapy can help minimize the symptoms of this condition.
What Are The Symptoms of Dyspareunia?

Some of the symptoms of painful sex (Dyspareunia) include:
But the most common symptom that women describe in relation to pain during intercourse is pain deep in the pelvic region or at the vaginal entrance.
In some cases, it may be a particular spot, while in others, it can radiate to the entire genital area. Some sensations most often experienced include “throbbing” or “burning.”
While there is usually no bleeding directly due to Dyspareunia per se (apart from mild spotting in the case of vaginal atrophy), if there is any bleeding during intercourse, it is most likely due to a specific medical issue, which is probably the cause of painful sex.
If you have bleeding during or after sexual intercourse, you should consult an OB-GYN to find the cause.
What Are The Symptoms of Dyspareunia?

Some of the symptoms of painful sex (Dyspareunia) include:
But the most common symptom women describe with pain during intercourse is pain deep in the pelvic region or at the vaginal entrance.
In some cases, it may be a particular spot, while in others, it can radiate to the entire genital area. Some sensations that women often experience include “throbbing” or “burning.”
While there is usually no bleeding due to Dyspareunia (apart from mild spotting in the case of vaginal atrophy), if there is, it is likely a medical issue.
If you have bleeding during or after sexual intercourse, you should consult an OB-GYN to find the cause. They will perform a pelvic exam to find the cause of the bleeding.
This exam usually includes examining your uterus, abdomen, pelvic region, and vagina.
Your doctor may also suggest a Pap test, rectal exam, and urine or vaginal fluid sample check for infection.
Sometimes, when there is no physical cause for pain during sex, it may be psychological.
Sexual therapy with or without your partner may help to resolve underlying issues surrounding past abuse, conflict, and associated intimacy issues.
Medications usually do not help with pelvic pain during or after sex.
However, medication can help with certain conditions.
For example, if the cause of your painful sex is vaginal atrophy or vaginal dryness associated with menopause or perimenopause, you may want to consider HRT or topical estrogen gels or cream in consultation with your doctor.
If there isn’t an apparent cause for your pelvic pain during sex.
We recommend physical therapy to explore whether postural misalignment, pelvic floor issues, or tight muscles may be causing your problems.
How Physical Therapy Can Improve Your Sex Life
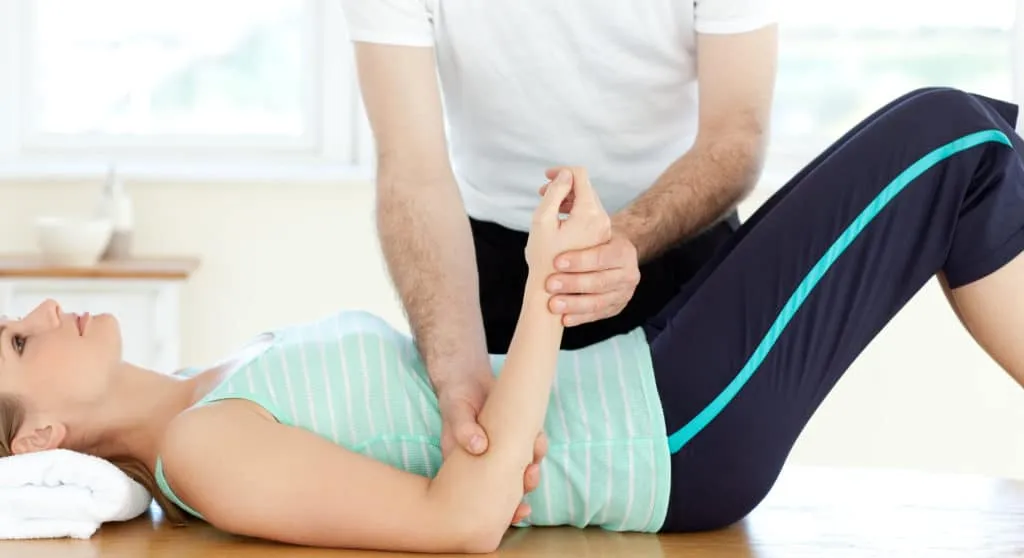

For healthy adults, sex is an integral part of life. Sexual intercourse and intimacy are as important as good nutrition and regular exercise for health and vitality.
Why? Because it builds and maintains your emotional connection with your partner, which reduces stress and tension, lowers anxiety, and increases your overall sense of well-being.
It also lowers blood pressure, contributes to heart health, and boosts your immune system. Of course, it should be enjoyable, too.
But pelvic pain during sex can make it a much less appealing prospect, leading many women who suffer to stop having sex altogether.
It doesn’t have to be that way. We can help.
As women’s health experts, we know that pelvic floor dysfunction is the leading cause of pain during sex.
When these muscles are weak, it can limit your ability to orgasm and enjoy sex.
Also, unstable ligaments and joints and lower back tension can contribute to pain during sexual intercourse.
But by the same token, having hypertonic (constantly contracted) pelvic floor muscles makes sex difficult and painful.
The good news is that with our help, you can retrain your pelvic floor muscles and strengthen and stabilize your lower back and core to make sex enjoyable again.
Apply for a FREE discovery visit today with one of our highly trained physical therapists.
The team at Universus PT look forward to welcoming you into our clinic some time soon.


